

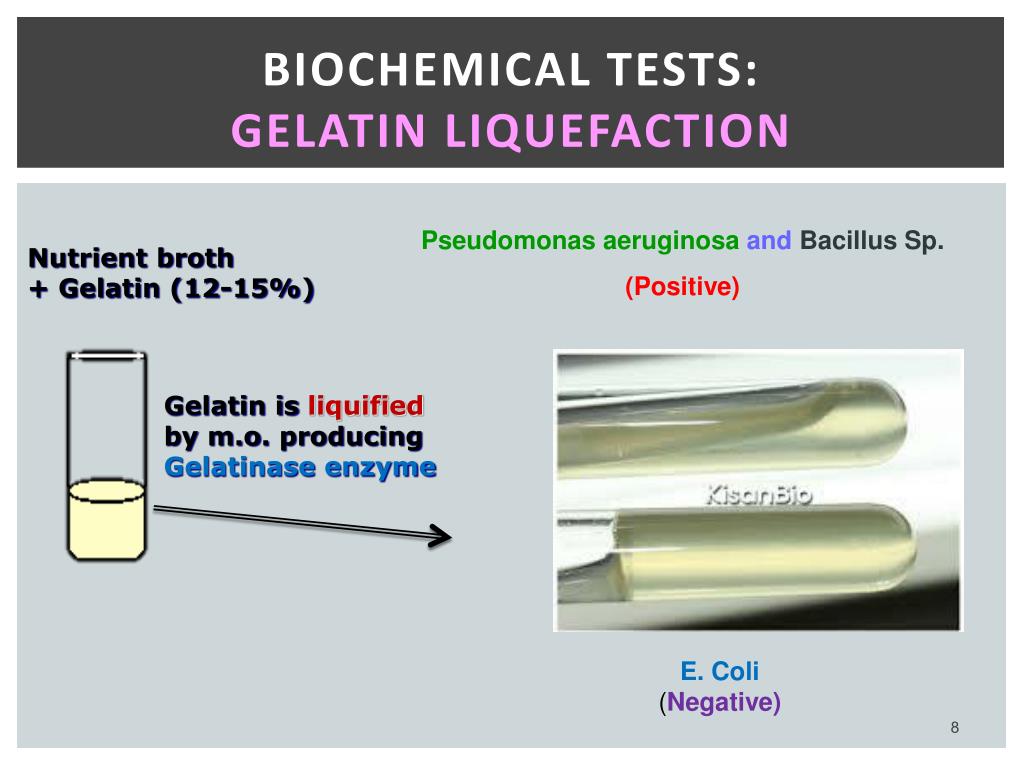
This test can be used to differentiate Serratia and Proteus species which are gelatin positive from other members of Enterobacteriaceae family.This test differentiates pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus which is gelatinase-positive from non-pathogenic epidermidis which is gelatinase negative.This test is helpful in identifying and differentiating species of Serratia, Proteus, Bacillus, Clostridium, Pseudomonas and Flavobacterium.This test is used to determine the ability of an organism that produce gelatinases.While the gelatinase negative organisms do not secrete enzymes and do not liquefy the medium. When nutrient gelatin tube is stab-inoculated with a gelatinase positive organisms, the secreted gelatinases will liquefy the gelatin, resulting in the liquefaction of the medium. This medium is a simple medium composed of gelatin, peptone and beef extract. The presence of gelatinases is detected using a nutrient gelatin medium. The amino acid is taken up by the cell and used for metabolic purposes. The reaction occurs in two sequential steps: in first reaction gelatinases hydrolyze gelatin into polypeptides and then polypeptides are further converted into amino acids as shown in figure. This test is used to determine the ability of an organism to produce extracellular proteolytic enzymes, gelatinases that hydrolyze gelatin. Gelatin dissolves in water at 50 degree Celsius and exists as liquid above 25☌ and solidifies or gels when cooled below 25☌. Robert Koch used nutrient gelatin as an early type of solid growth medium.
It has been used as a solidifying agent in food for a long time. Gelatin is a protein derived from the animal protein collagen, a component of connective tissue and tendons in human and other animals. Please Rate 0 1 2 3 4 5 Gelatin Hydrolysis Test- Principle, Uses, Media, Procedure and Result


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
